INtime Distributed RTOS
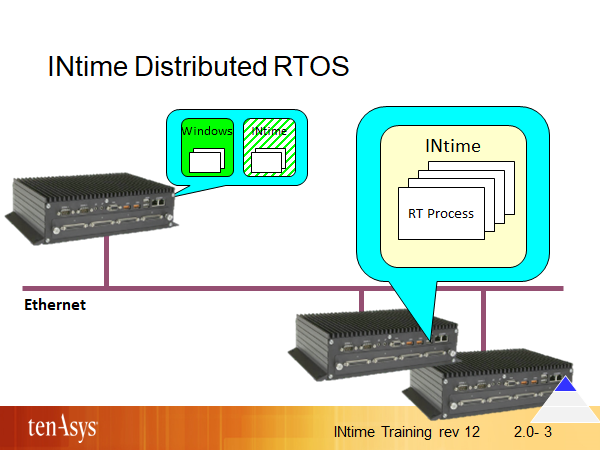
An INtime node running on a host in the INtime Distributed RTOS configuration (i.e. the host does not run a Windows node) is called D-RTOS node. D-RTOS nodes may be connected via Ethernet to a Windows host and utilize the real-time TCP/IP stack for the connection.
In the case of systems that contain D-RTOS nodes, the Windows host may or may not include an INtime node, it is an optional feature. Certainly, the NTX element (RT interface extensions for Windows) must always be present on the Windows host.
It is not required that the Windows host always be present. That is, the host is allowed to “go down” and this will not stop a D-RTOS node. Of course, if an INtime node depends on some special service from the host (such as sharing information with a Windows application) then the INtime node will be impacted by the host “going down”.
A key difference between D-RTOS nodes and INtime nodes in an “INtime for Windows” configuration is that the Windows host can disappear and reappear without requiring a restart of a D-RTOS node (the real-time subsystem). Likewise, the D-RTOS node utilizes dedicated hardware and does not need to ensure that sufficient core cycles are provided for running Windows, a requirement for a shared core, so the real-time application can consume all core cycles.